Motors for wheels
Two motors are used to steer the wheels. They can run independently, what enables Robbie to move forward, backward and to turn right or turn left.
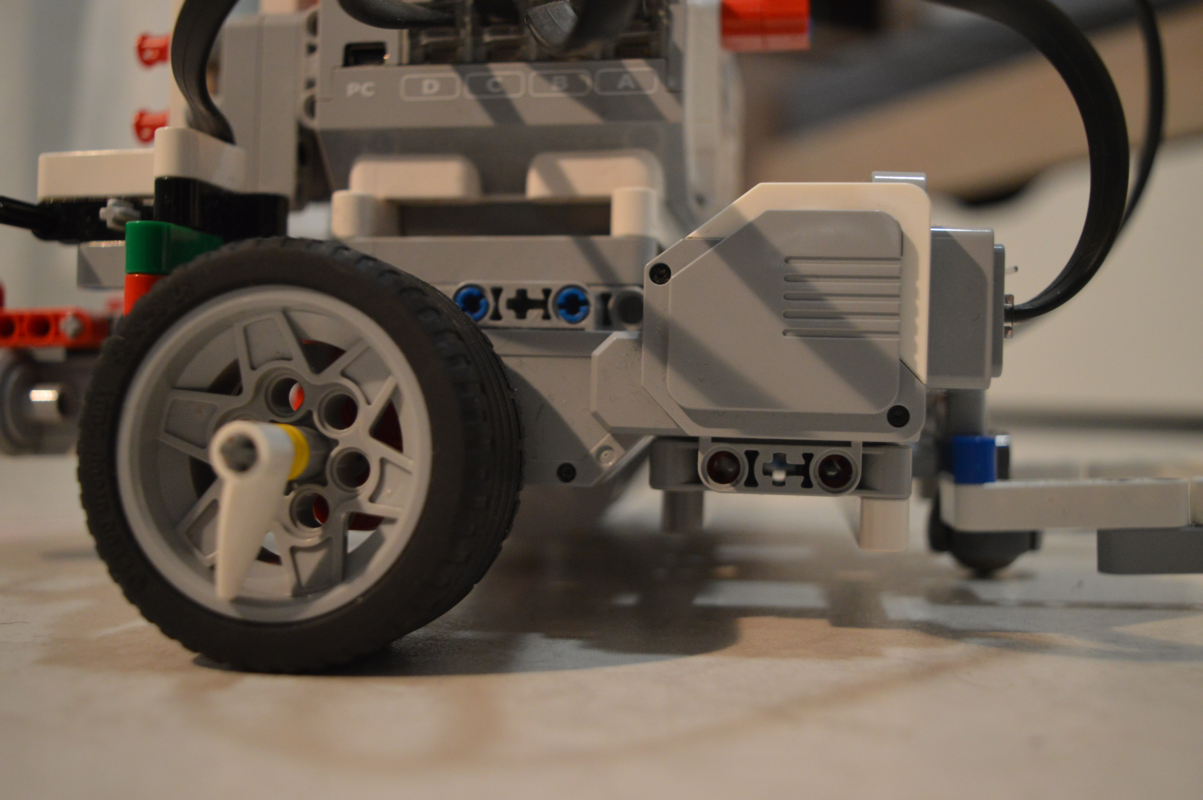

Robbie is using 4 motors and 3/4 sensors to achieve the cartography of the space :
a sonar, a color sensor and an accelerometer.
Thanks to our own design, the robot is included in a circle, the diameter of which is the length between the wheels.
Robbie stays in the circle when it turns, that is a guarantee of safety.
Two motors are used to steer the wheels. They can run independently, what enables Robbie to move forward, backward and to turn right or turn left.

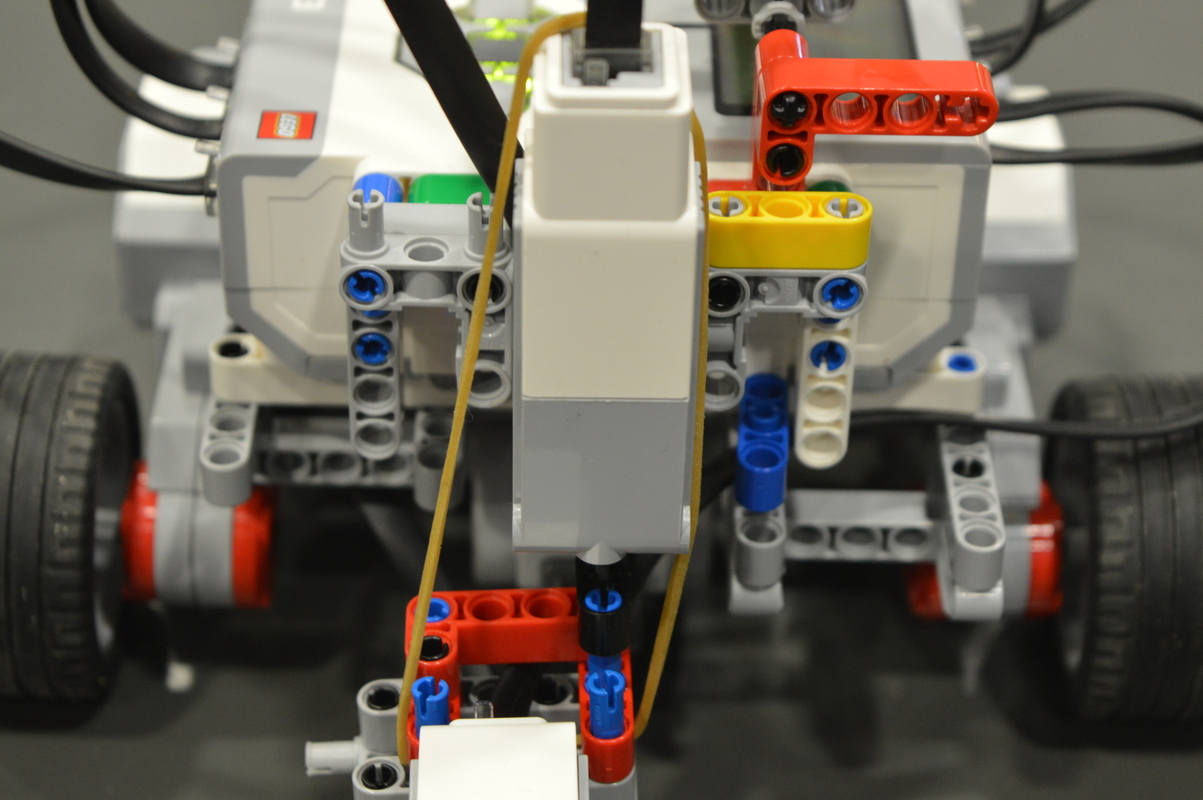
A third servomotor manages an axis on which are fixed the sonar and the color sensor.
These two sensors can move independently from the body of Robbie and hence scan the environment when the robot is moving.
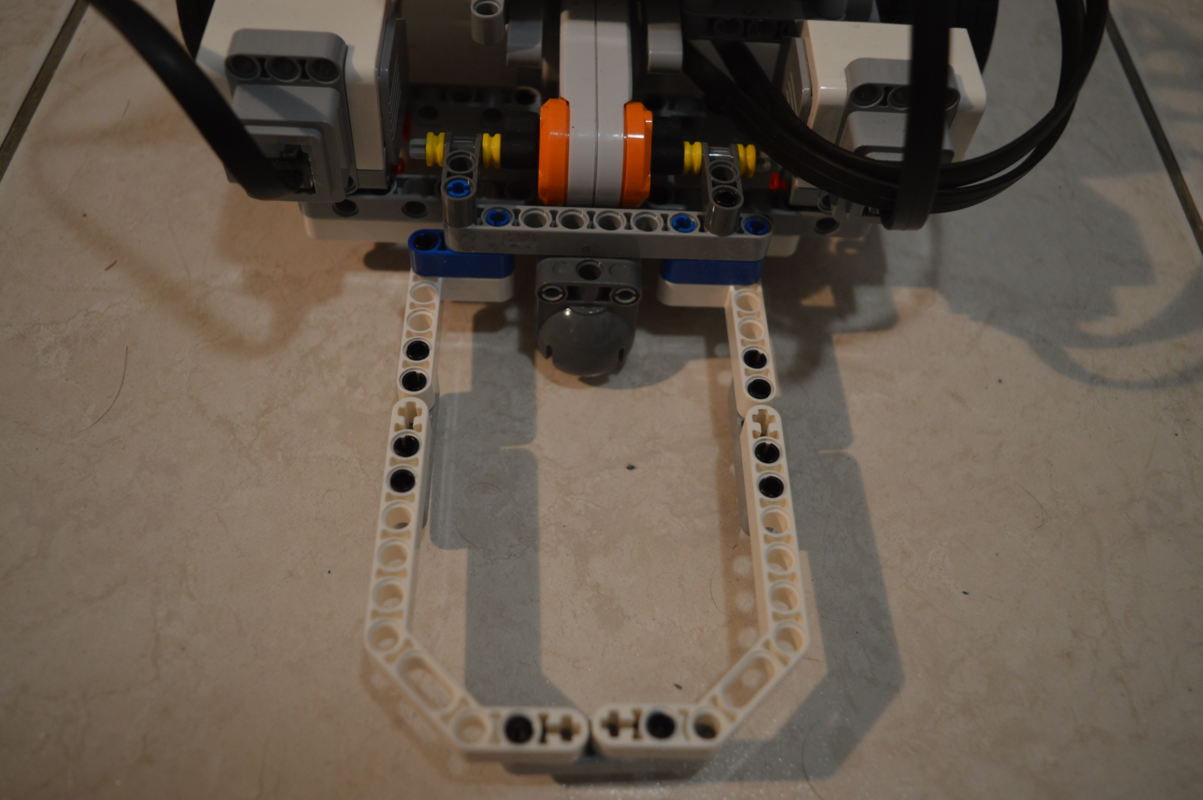
The fourth and last motor manages an arm that is located at the back of the robot. It has two possible positions : up and down.
When the arm is up, it is located in the circle defined by the body of Robbie. When the arm is down, it can catch balls and move them.
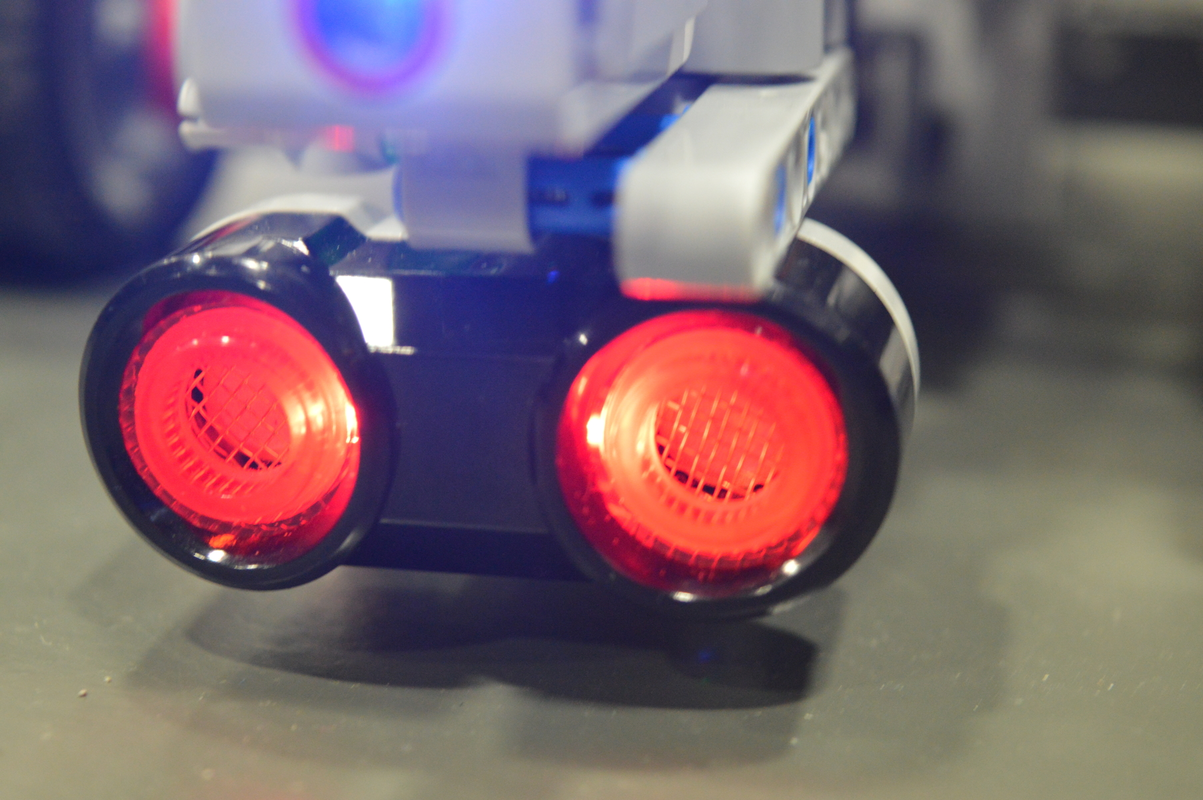

The sonar is located on the front of the robot and can move to both sides. It measures the distance between Robbie and any obstacle in front of it. This captor is mainly used for detection of obstacles and positioning.
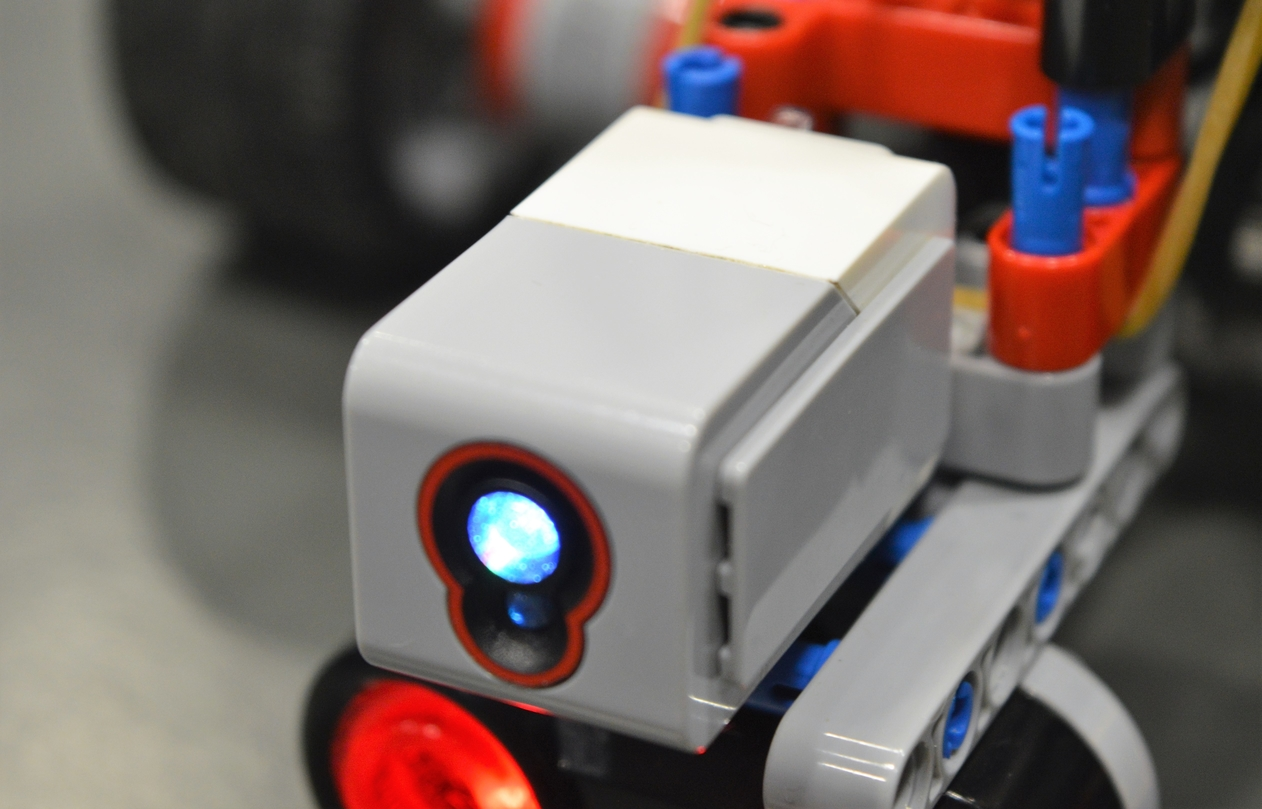
The color sensor is located just next to the sonar and can also move due to a servomotor. The sensor is used to analyze the color of obstacles and differentiate non-movable objects from movable objects (which are red).
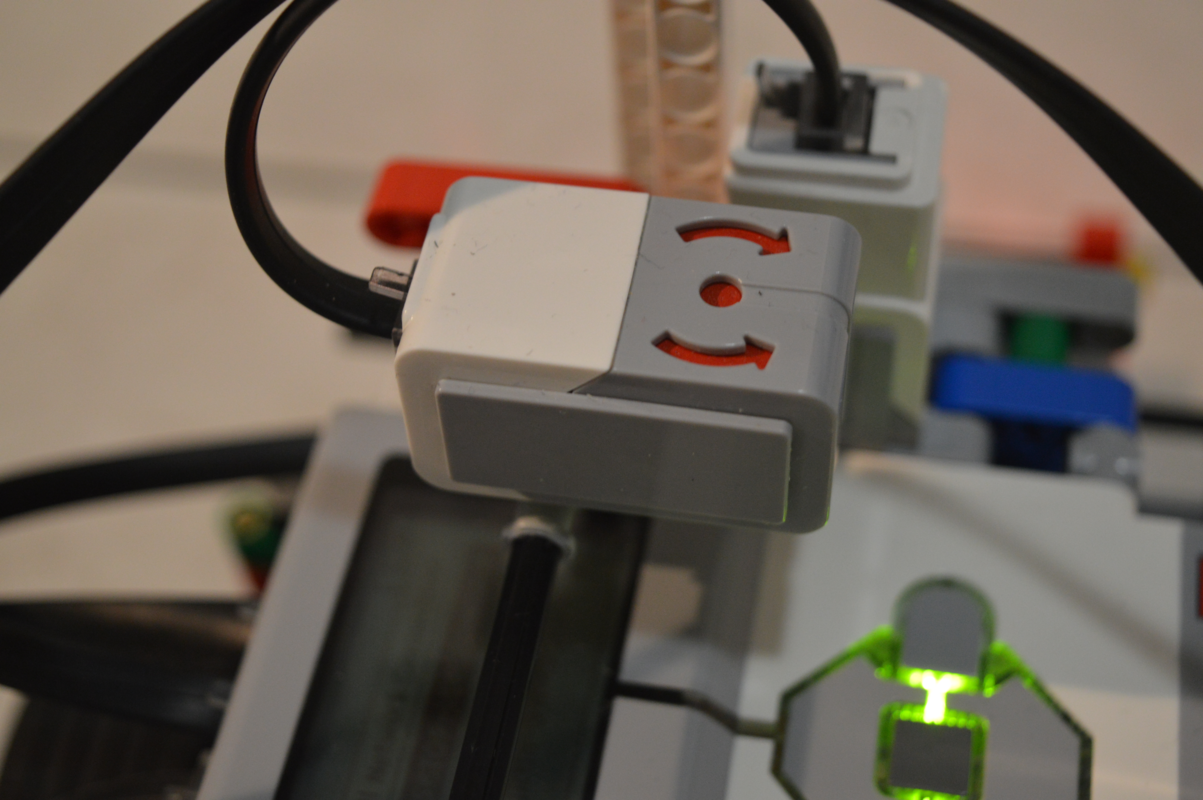


The gyroscope is fixed on the top of the robot, exactly between the wheels. It is used to correct the rotation of the robot for large angles.